
TL;DR Peer-to-Peer (P2P) means two parties connect and exchange value (files, money, messages, etc.) directly without a middleman. In crypto, P2P trading lets you buy/sell Bitcoin or altcoins straight from another person using almost any payment method. It is cheaper, more private, and censorship-resistant than centralized exchanges, but comes with risks like scams that you must learn to manage.
The term “peer-to-peer” first became famous with file-sharing programs like Napster and BitTorrent in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Instead of downloading a music file from a central server owned by a company, your computer (a peer) connected directly to another user’s computer (another peer) and swapped the file.
In simple words:
This idea later jumped from file-sharing to money (Bitcoin) and now powers most of decentralized finance.
A node is any device (computer, phone, server) running the P2P software. Types of nodes in crypto:
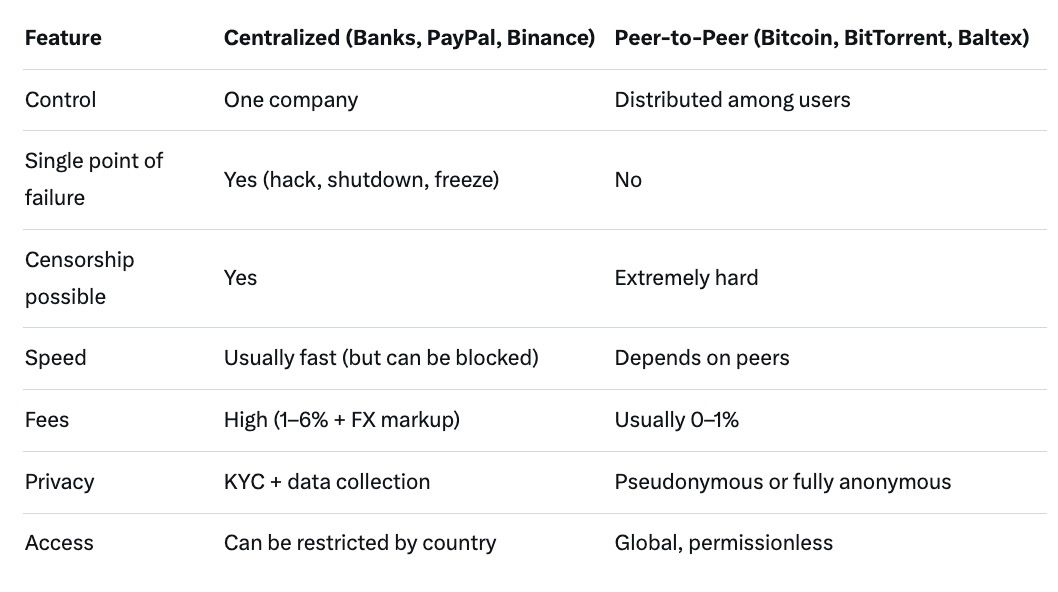
Not all “P2P” networks are equally decentralized: Fully decentralized → Bitcoin, Monero, BitTorrent Mostly decentralized → Ethereum (after The Merge still needs many nodes) Hybrid → Some DeFi protocols that still rely on centralized oracles Centralized “P2P” marketing → Many exchanges that say “P2P” but actually escrow everything themselves
In true P2P you send value straight from your wallet to another person’s wallet. No third party can freeze, reverse, or take a big cut (except network fees).
If dispute → arbitrators (humans) look at chat + proof and decide.
Popular escrow methods in 2025:
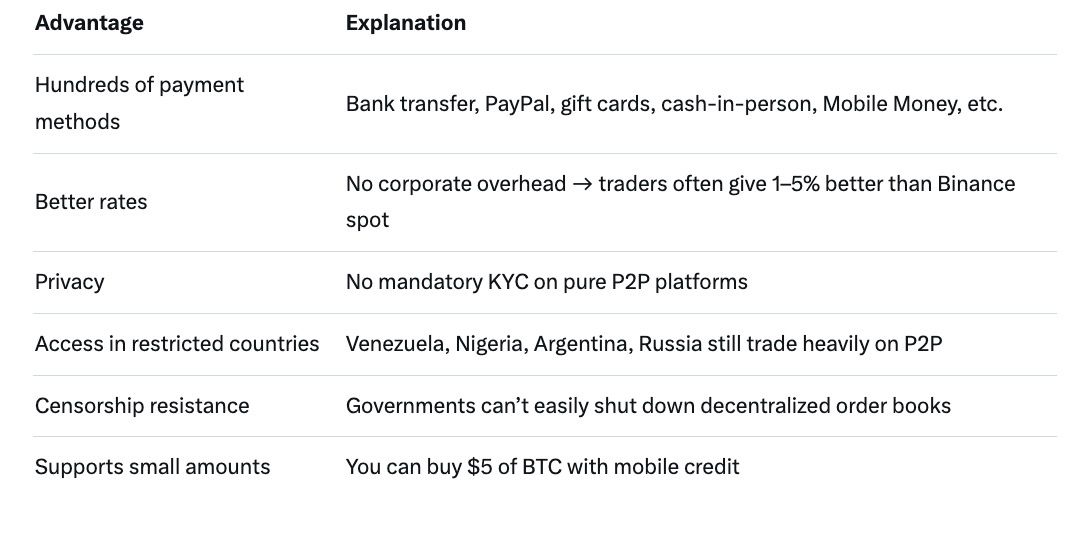

Pro tip: In 2025 the safest P2P platforms show:
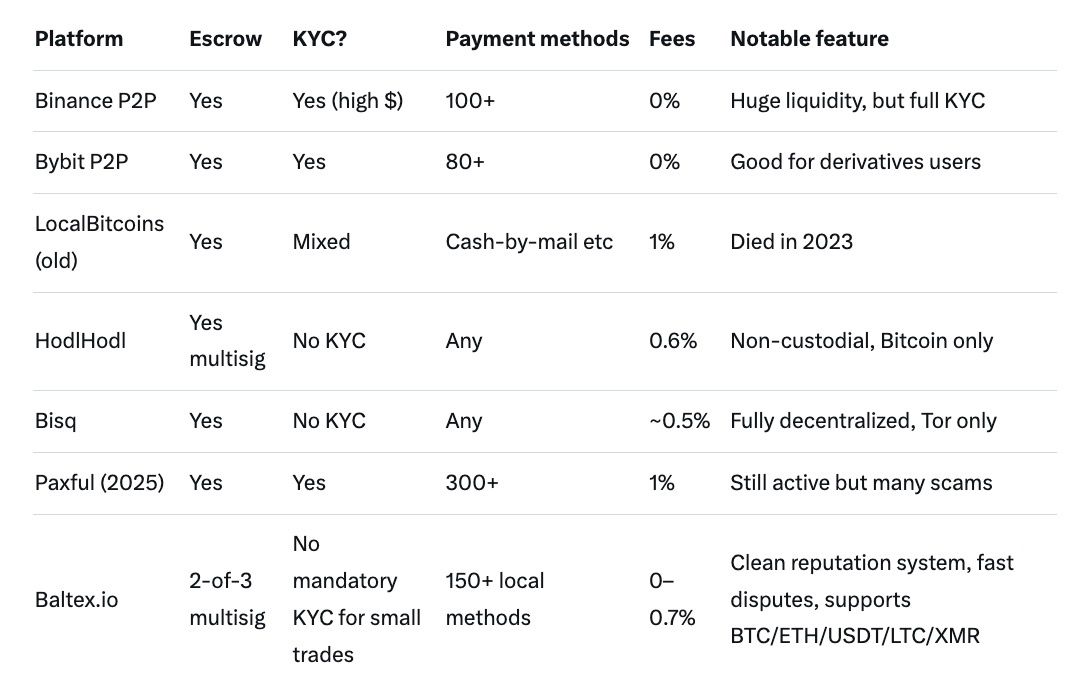
Baltex.io has become one of the go-to options in 2025 for users who want a middle ground: strong escrow, optional KYC only above certain limits, and support for privacy coins like Monero.
Q: Is P2P trading legal? A: In most countries yes (including USA, EU, India). A few countries (e.g., Bolivia) ban crypto entirely. Trading itself is rarely illegal; the platform jurisdiction matters.
Q: Can I get scammed even with escrow? A: Yes, if the platform’s dispute team is bad. That’s why reputation >200 trades and 99%+ rating is crucial.
Q: Do I pay taxes on P2P trades? A: Same rules as centralized exchanges in almost every country. Keep records.
Q: Which payment methods are safest in 2025? A: Bank transfer (same bank is best), cash deposit, USDT on TRC20/BEP20, gift cards only with very trusted traders.
Q: Can I trade anonymously? A: Yes on no-KYC platforms (HodlHodl, Bisq, Baltex.io below limits, LocalMonero, etc.).
Peer-to-Peer is not just a technical architecture — it is the original promise of cryptocurrency: financial sovereignty, censorship resistance, and global access without gatekeepers.
While centralized exchanges still dominate trading volume because of convenience, P2P remains the most resilient and private way to acquire Bitcoin and altcoins in 2025. Whether you are in a country with capital controls, want to preserve privacy, or simply hate paying 4% credit-card fees, P2P trading gives you options that no bank or big exchange can match.
Start small, trade only with high-reputation users, always wait for escrow, and you’ll discover why millions of people worldwide moved billions of dollars peer-to-peer this year — quietly, cheaply, and without asking for permission.
Ready to try? Platforms like Baltex.io, Hodl Hodl, and Bisq are waiting with open (decentralized) arms.
Happy trading — and stay safe out there!