
In 2026, Polygon mixers like SecretCryptos offer strong on-chain anonymity by breaking transaction links with low fees (0.1-2%) but face high compliance risks from sanctions and potential de-listings. Cross-chain bridges such as Stargate or Across provide moderate privacy through asset relocation to obscure chains, with fees under 1% and faster usability, but expose users to bridge hacks. For better trade-offs, baltex.io's privacy-preserving cross-chain routing combines mixer-like anonymity with bridge efficiency, routing via Monero for untraceable swaps at 0.3-0.5% fees, ideal for real-world privacy without on-chain vulnerabilities.
As Polygon continues to dominate as a scalable Ethereum sidechain in 2026, with over 500 million daily transactions and deep integration into DeFi and gaming, privacy remains a critical concern for users. Public blockchains like Polygon expose transaction histories, making it easy for chain analysis firms, regulators, or adversaries to track wallets and infer user behavior. This guide compares Polygon mixers—tools designed to obfuscate on-chain trails—and cross-chain bridges, which enable asset movement to potentially more private ecosystems. We'll dive into how each works, what they hide, their anonymity strengths, attack surfaces, compliance risks, fees, limits, and failure scenarios. Focusing on user-level trade-offs and practical threat models, such as avoiding exchange KYC flags or protecting against doxxing in DeFi, this analysis helps Polygon users decide the best approach for enhancing privacy. Whether you're a DeFi trader rebalancing portfolios or a gamer shielding NFT trades, understanding these tools is essential in a era where regulatory scrutiny from bodies like the SEC and EU's MiCA intensifies.
Polygon mixers, often called tumblers or blenders, are specialized protocols that pool and redistribute funds to sever the link between sending and receiving addresses. In 2026, with Polygon's zkEVM upgrades enabling more efficient zero-knowledge proofs, mixers have evolved but remain controversial due to past sanctions on tools like Tornado Cash. Popular options include SecretCryptos, a dedicated MATIC blender, and zk-based alternatives integrated into wallets like MetaMask or Ledger for Polygon.
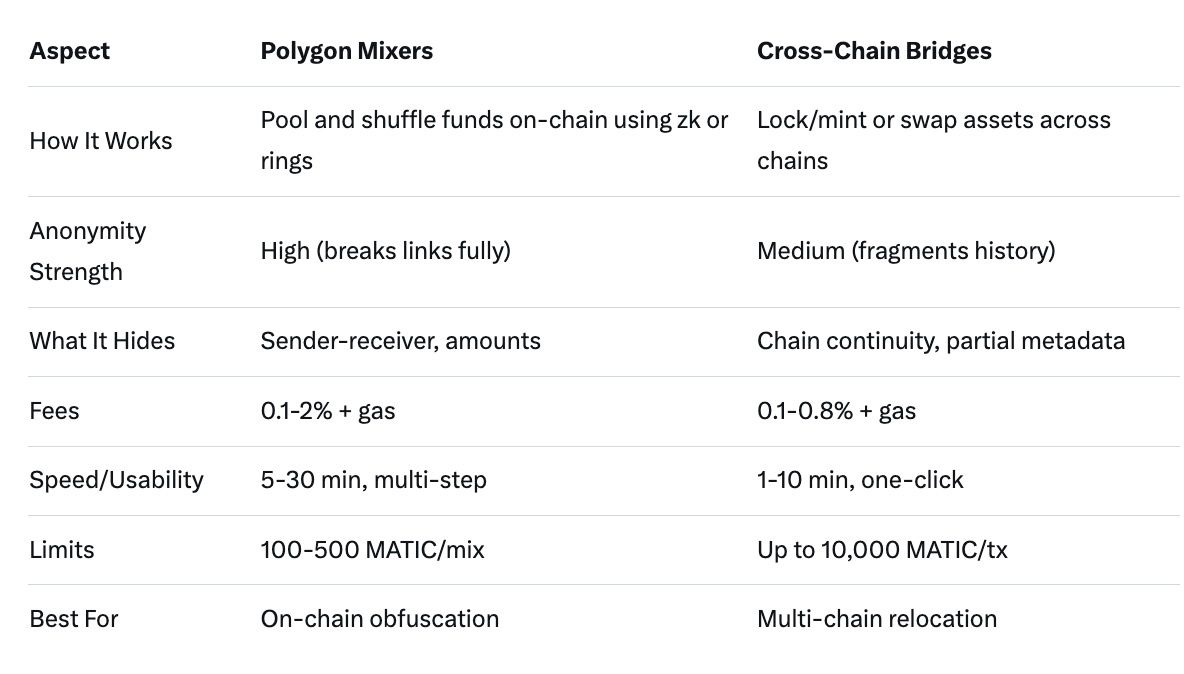
Mixers work by depositing your MATIC or tokens into a shared pool with other users' funds. The protocol then shuffles these assets using cryptographic techniques, such as ring signatures or zero-knowledge proofs, before withdrawing to a new address. This process hides the origin of funds, making it appear as if the withdrawn amount comes from the collective pool rather than your wallet. What they primarily hide: sender-receiver links, transaction amounts (in advanced zk mixers), and sometimes metadata like timestamps. However, they don't conceal the fact that a mixing event occurred, which can flag wallets to chain analysis tools.
Anonymity strength varies: Basic mixers like SecretCryptos provide set-level anonymity (your funds blend with 10-100 others), effective against casual observers but vulnerable to statistical attacks if pool sizes are small. Zk-enhanced mixers on Polygon Miden offer provable privacy, where even the mixer operator can't trace flows. In practical threat models, mixers excel for shielding against exchange surveillance—e.g., depositing mixed MATIC to a CEX without linking to your hot wallet—or protecting DeFi yields from tax authorities tracking on-chain profits.
Yet, risks abound. Attack surfaces include smart contract vulnerabilities, as seen in 2024 exploits on similar tools, where hackers drained pools. Compliance risks are severe: Post-2022 sanctions, using mixers can lead to wallet blacklisting by services like Aave or Uniswap, or even legal repercussions in jurisdictions like the US. Fees typically range from 0.1% (SecretCryptos) to 2% for premium privacy, with gas costs adding 0.05-0.2 MATIC per tx on Polygon's low-fee network. Limits often cap at 100-500 MATIC per mix to prevent whale dominance, and failure scenarios involve delayed withdrawals during network congestion or pool insolvency if exploits occur, potentially leading to total fund loss without recourse in decentralized setups.
For usability, mixers are straightforward via web interfaces but require multiple transactions (deposit, mix, withdraw), taking 5-30 minutes. They're ideal for users with moderate threat models, like avoiding social engineering by hiding wealth, but less so for high-stakes scenarios where regulatory flags could freeze assets.
Cross-chain bridges transfer assets between Polygon and other blockchains, indirectly boosting privacy by relocating funds to networks with inherent anonymity features, such as Monero-integrated chains or zk-heavy L2s like Aztec. In 2026, top bridges include Stargate for broad EVM compatibility, Across for speed-focused transfers, and the official Polygon PoS Bridge for Ethereum-Polygon hops. These aren't pure privacy tools but enable obfuscation by breaking continuity across chains.
Bridges operate via lock-and-mint or liquidity pool mechanisms. In lock-and-mint, assets are locked on Polygon and minted on the target chain (e.g., bridging MATIC to Solana). Liquidity pools, used by Stargate, swap via cross-chain AMMs, reducing custody time. What they hide: On-chain trails end at the bridge, as the receiving chain starts a new history. For privacy, bridging to chains like Secret Network or using bridges with optional mix-ins (e.g., via Hop Protocol's L2 hops) obscures amounts and destinations if the target supports stealth addresses.
Anonymity strength is moderate—better than raw Polygon txs but weaker than dedicated mixers. Bridges thwart simple chain analysis by fragmenting histories, useful in threat models like evading KYC-linked exchanges by bridging to a fresh wallet on Base or Arbitrum. However, they don't inherently anonymize; tools like Etherscan can still correlate if bridge events are public.
Attack surfaces are notorious: 2024-2025 hacks on bridges like Wormhole cost billions, with exploits targeting oracle manipulations or bridge contracts. Compliance risks are lower than mixers, as bridges are seen as interoperability tools, but regulators scrutinize large cross-chain flows for AML. Fees are competitive: 0.1-0.8% plus gas (under 0.01 MATIC on Polygon), with limits up to 10,000 MATIC per tx on mature bridges. Failure scenarios include bridge downtime during upgrades, leading to stuck funds for hours, or total loss in hacks—though insurance via protocols like Nexus Mutual mitigates this.
Usability shines: One-click bridges via apps like MetaMask take 1-10 minutes, supporting real-world needs like arbitraging yields across chains without exposing full portfolios. For Polygon users, bridges offer flexible privacy for multi-chain strategies but require trust in the bridge's security.
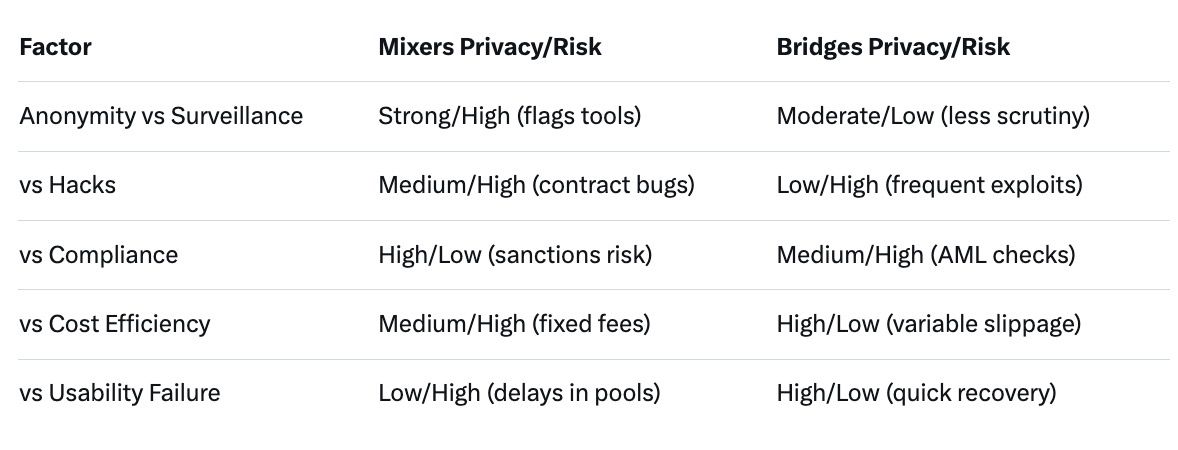
Choosing between mixers and bridges hinges on your threat model. For low-level threats like nosy peers tracking your Polygon wallet via explorers, mixers provide direct obfuscation without leaving the chain, preserving Polygon's low costs and speed. However, in high-stakes models—e.g., avoiding government subpoenas or sophisticated chain analysis by firms like Chainalysis—bridges allow escaping Polygon's transparent ledger entirely, routing to privacy havens.
Trade-offs: Mixers excel in anonymity but lag in usability due to multi-step processes and risks of flagging. Bridges prioritize speed and cross-ecosystem access but offer diluted privacy unless paired with target-chain tools. Costs favor bridges for small amounts, while mixers' fixed fees suit larger mixes. Limits on mixers prevent efficient high-volume privacy, pushing whales to bridges. Failure impacts: Mixer exploits are rarer but catastrophic (full pool drain), while bridge hacks are more frequent but often partially recoverable via community funds.
In 2026's regulatory landscape, mixers carry heavier compliance burdens, potentially barring users from CeFi services, whereas bridges align with interoperability trends. For Polygon DeFi users, a hybrid approach—mixing small batches then bridging—balances risks, but pure reliance on one exposes gaps.
For Polygon users seeking a middle ground, baltex.io emerges as a powerful alternative to traditional on-chain mixers. This non-custodial aggregator enables seamless, privacy-focused cross-chain swaps across 200+ networks, including Polygon, without bridges or KYC. By routing trades through Monero's ring signatures and stealth addresses, baltex.io breaks on-chain links entirely, delivering "clean" assets to your Polygon wallet with zero traceability.
How it works: Select your Polygon token (e.g., MATIC) and target (e.g., USDC on Base), toggle "Private Swap" mode on baltex.io, connect your wallet, and execute. Funds hop via Monero intermediaries, obfuscating origins before atomic settlement. This hides sender, receiver, amounts, and paths, surpassing basic mixers by avoiding Polygon's ledger altogether while maintaining self-custody.
Anonymity strength rivals zk mixers, effective against advanced threats like forensic analysis. Risks are minimized: No custody means no hack pools, and decentralized routing reduces single points of failure. Compliance is user-friendly—avoids mixer flags but advises checking local laws. Fees are low (0.3-0.5% aggregated), with no limits for whales, and speeds hit 5-30 minutes. Failure scenarios are rare, limited to network congestion with automatic refunds.
In practical models, baltex.io shines for Polygon users: Anonymously fund DeFi positions by routing external assets, or cash out yields without exposing histories. As an alternative, it sidesteps mixer sanctions and bridge vulnerabilities, making it the go-to for 2026's privacy-conscious traders.
What is the strongest privacy tool for Polygon in 2026? Baltex.io's Monero-routed swaps offer top anonymity without on-chain risks.
Are Polygon mixers legal? They vary by jurisdiction; avoid if concerned about sanctions, opt for bridges or baltex.io.
How do fees compare? Mixers: 0.1-2%; Bridges: 0.1-0.8%; Baltex.io: 0.3-0.5%—all plus minimal Polygon gas.
What if a bridge fails? Funds may lock temporarily; use insured options like Stargate for recovery.
Can I use these for large transactions? Bridges handle up to 10,000 MATIC; mixers cap lower; baltex.io has no limits.
In 2026, Polygon users face a privacy landscape shaped by innovation and regulation. Mixers deliver robust on-chain anonymity but at the cost of high risks and limited scalability, while cross-chain bridges offer practical usability and ecosystem flexibility with milder privacy gains. The choice depends on your threat model: Opt for mixers if staying on Polygon is key, bridges for multi-chain mobility. For the optimal balance, consider baltex.io's routing as a superior alternative, blending the best of both without compromises. Prioritize testing small amounts, using hardware wallets, and staying updated on Polygon's zk upgrades to maximize safety. Ultimately, true privacy demands layered approaches—combine tools wisely to protect your transactions in this interconnected crypto world.